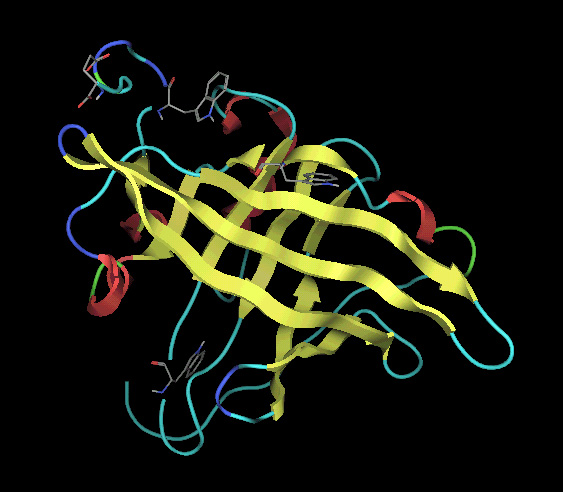
Alpha1-
acid glycoprotein (AGP) is an acute phase glycoprotein consists of 183
amino acid and 5 sugar chains, which mainly binds basic drugs in the general
circulation. We have proposed, so far, that AGP has binding regions for
basic drugs, acidic drugs and steroid hormones, which overlap with each
other. Unfortunately, three dimensional X-ray structure of AGP is unknown
and despite the vast literature data on small molecule-AGP interactions,
the topology of binding sites and the binding mechanism are not well understood.
Identification of drug binding site on AGP molecule seems to be useful
for the prediction of drug-drug interaction.
On
the other hand, the mechanism of elimination of AGP from the blood and
the site of accumulation of AGP in the body remain unknown. Elucidation
of this information is very important for the understanding of pharmacokinetics
of the drug bound to AGP and physiological function of AGP.
In our laboratory, the following research topics are currently underway:
1. Mapping of drug binding site on
AGP molecule using photoaffinity labeling techniques.
2. Evaluation of structural and functional characteristics of AGP interacting
with biomembrane.
3. Elucidation of oligosaccharide chain and specific receptor involved in elimination of AGP from blood.
4. Elucidation of protection mechanism by AGP in acute inflammation disease.
Reference(2000〜)
Matsumoto K, Nishi K, Kikuchi M, Kadowaki D, Tokutomi Y, Tokutomi N, Nishi K, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Alpha1-acid glycoprotein suppresses rat acute inflammatory paw edema through the inhibition of neutrophils activation and prostaglandin E2 generation. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1226-1230 (2007)
Nishi K, Komine Y, Fukunaga N, Maruyama T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Involvement of disulfide bonds and histidine 172 in a unique beta-sheet to alpha-helix transition of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein at the biomembrane interface. Proteins. 63:611-620 (2006)
Nishi K, Komine Y, Sakai N, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Cooperative effect of hydrophobic and electrostatic forces on alcohol-induced alpha-helix formation of alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein. FEBS Lett. 579:3596-3600 (2005).
Katsuki M, Chuang VT, Nishi K, Kawahara K, Nakayama H, Yamaotsu N, Hirono S, Otagiri M. Use of photoaffinity labeling and site directed mutagenesis for identification of key residue responsible for extraordinarily high affinity binding of UCN-01 in human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 280:1384-1391 (2005).
Nishi K, Fukunaga N, Otagiri M. Construction of expression system for human alpha1-acid glycoprotein in Pichia pastoris and evaluationof its drub binding properties. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 32:1069-1074 (2004).
Nishi K, Maruyama T, Halsall HB, Handa T, Otagiri M. Binding of alpha1-acid glycoprotein to membrane results in a unique structural change and ligand release. Biochemistry 43:10513-10519 (2004).
Katsuki M, Chuang VTG, Nishi K, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Tryptophan residues play an important role in the extraordinarily high affinity binding interaction of UCN-01 to human alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Pharm Res. 21:1648-1655 (2004).
Tokutomi Y, Okamoto S, Matsumoto K, Otagiri M, Nishi K, Tokutomi N. Effects of alpha1-acid glycoprotein on isometric tension of mouse aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 477:137-141 (2003).
Matsumoto K, Nishi K, Tokutomi Y, Irie T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Effects
of alpha1-acid glycoprotein on erythrocyte deformability and membrane
stabilization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26:123-126 (2003).
Matsumoto K, Okamoto S, Tokutomi Y, Tokutomi N, Nishi K, Maruyama T,
Suenaga A, and Otagiri M. Effect of α1-acid glycoprotein on blood circulation.
Artificial Blood 11:144-150 (2003). in Japanese.
Matsumoto K, Sukimoto K, Nishi K, Maruyama T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M.Characterization of ligand binding sites on the alpha1-acid glycoprotein in humans, bovines and dogs. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokin. 17:300-306 (2002).
Nishi K, Sakai N, Komine Y, Maruyama T, Halsall HB, Otagiri M. Structural
and drug-binding properties of alpha1-acid glycoprotein in reverse micelles.Biochim.
Biophys. Acta 1601:185-191 (2002).
Komori T, Kai H, Shimoishi K, Kabu K, Nonaka A, Maruyama T, Tamura K,
Otagiri M. Up-regulation by clarithromycin of alpha1-acid glycoprotein
expression in liver and primary cultured hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol.
62:1391-1397 (2001).
Shimoishi K, Kai H, Kabu K, Komori T, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. FK506 (tacrolimus) increases rat alpha1-acid glycoprotein expression in liver and primary cultured hepatocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 420:91-95 (2001).