 |
|||
|
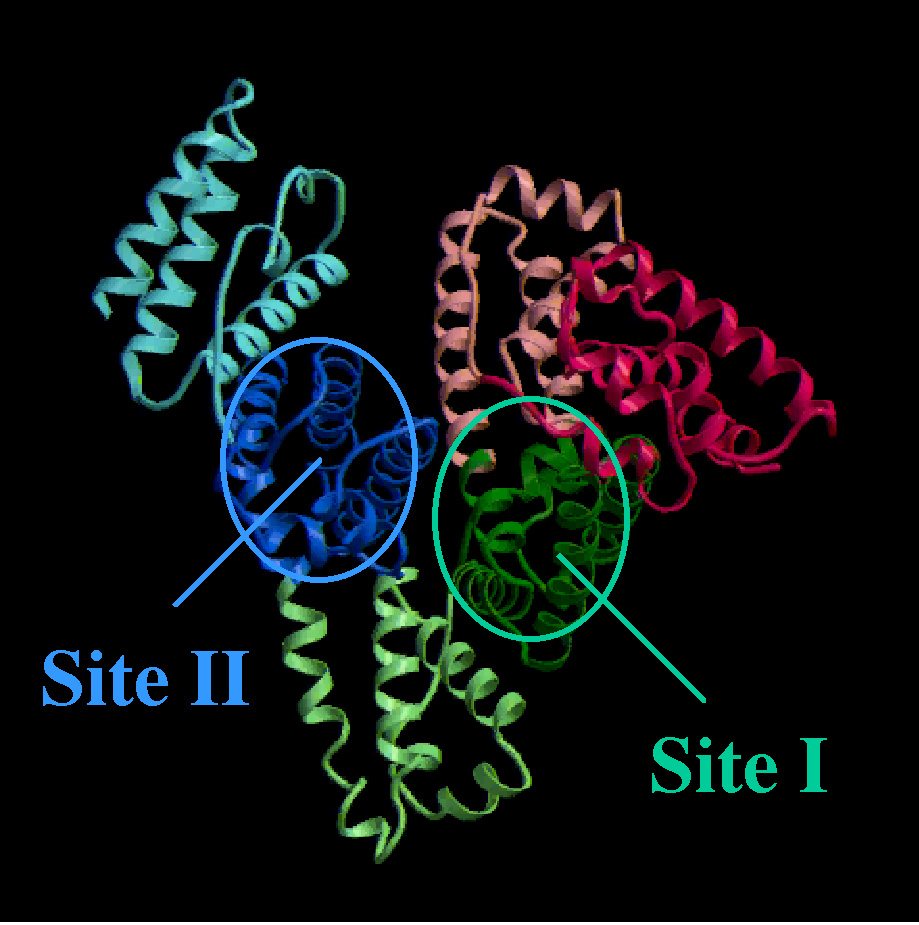
Binding sites of HSA
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Tremendous advances have been achieved in the past 20 years in our understanding of human serum albumin (HSA). HSA has been a topic of intense research for scientists from various fields as it is the most abundant plasma protein and easy to isolate. It is well known for its extraordinary binding capacity for both endogenous and exogenous substances, including a wide range of drugs. Binding of drugs to HSA in the circulatory system is an important factor which determines the pharmacokinetisc and pharmacological effect of drugs. Most drugs specifically interact with either two major drug binding sites, termed as site I and site II, on HSA. Recent x-ray crystallographic structure of HSA successfully showed that the location of site I and site II is at subdomain IIA and IIIA, respectively. However, in view of most functional proteins exhibit structural dynamics during their functional activities, static structural information such as x-ray crystallographic data can not completely reveal the structure-function relationship of the protein. We thus examine the structural and functional properties of HSA using various techniques ranging from spectrometry to site-direct mutagenesis. Protein engineering can be defined as the use of genetic and chemical techniques to change the structure and function of a protein, thus producing a novel product with specific, desired, properties. With the structural and functional data, we proceed to design novel recombinant albumin with specific pharmaceutical utility of therapeutic applications. In our research strategy, we have subdivided this main theme into
3 research topics: 1. Topology analysis of the drug binding sites on HSA using spectrometry, biochemical, molecular biological and computational modeling techniques.
Reference(2000〜) Kitamura R, Asanoma H, Nagayama S, Otagiri M. Identification of human liver cytochrome P450 isoforms involved in autoinduced metabolism of the anti-angiogenic agent TSU-68 ((Z)-5-[(1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-propanoic acid). Drug Metab Dispos. In press (2008) Katayama N, Nakajou K, Komori H, Uchida K, Yokoe J, Yasui N, Yamamoto H, Kai T, Sato M, Nakagawa T, Takeya M, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Design and evaluation of S-nitrosylated human serum albumin as a novel anticancer drug. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 325, 69-76, (2008) Inoue K, Nakai Y, Ueda S, Kamigaso S, Ohta KY, Hatakeyama M, Hayashi Y, Otagiri M, Yuasa H. Functional characterization of PCFT/HCP1 as the molecular entity of the carrier-mediated intestinal folate transport system in the rat model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver. Physiol., 294, 660-668, (2008) Anraku, M., Kouno, Y., Kai, T., Tsurusaki, Y., Yamasaki, K., and Otagiri, M. The role of N-acetyl-methioninate as a new stabilizer for albumin products. Int. J. Pharm,. 329, 19-24, (2007) Chuang, V. T., and Otagiri, M. Recombinant human serum albumin. Drugs Today (Barc), 43, 547-561, (2007) Ishima, Y., Akaike, T., Kragh-Hansen, U., Hiroyama, S., Sawa, T., Maruyama, T., Kai, T., and Otagiri, M. Effects of endogenous ligands on the biological role of human serum albumin in S-nitrosylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 364, 790-795, (2007)
Ishima Y, Sawa T, Kragh-Hansen U, Miyamoto Y, Matsushita S, Akaike T, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links S-Nitrosylation of human variant albumin Liprizzi (R410C) confers potent antibacterial and cytoprotective properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:969-977 (2007) Anraku M, Kouno Y, Kai T, Tsurusaki Y, Yamasaki K, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links The role of N-acetyl-methioninate as a new stabilizer for albumin products. Int J Pharm. 329:19-24 (2007) Mera K, Nagai R, Haraguchi N, Fujiwara Y, Araki T, Sakata N, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Hypochlorous acid generates N epsilon-(carboxymethyl)lysine from Amadori products. Free Radic Res. 41:713-718 (2007) Kragh-Hansen U, Watanabe H, Nakajou K, Iwao Y, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Chain length-dependent binding of fatty acid anions to human serum albumin studied by site-directed mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 363:702-712 (2006) Matsushita S, Chuang VT, Kanazawa M, Tanase S, Kawai K, Maruyama T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Recombinant human serum albumin dimer has high blood circulation activity and low vascular permeability in comparison with native human serum albumin. Pharm Res.23:882-891 (2006) Chuang VT, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Stereoselective binding of human serum albumin. Chirality.18:159-166 (2006) Iwao Y, Anraku M, Hiraike M, Kawai K, Nakajou K, Kai T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links The structural and pharmacokinetic properties of oxidized human serum albumin, advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP). Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 21:140-146 (2006) Iwao Y, Anraku M, Yamasaki K, Kragh-Hansen U, Kawai K, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Oxidation of Arg-410 promotes the elimination of human serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1764:743-739 (2006) Mera K, Anraku M, Kitamura K, Nakajou K, Maruyama T, Tomita K, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Oxidation and carboxy methyl lysine-modification of albumin: possible involvement in the progression of oxidative stress in hemodialysis patients. Hypertens Res. 28:973-980 (2005) Otagiri M. A molecular functional study on the interactions
of drugs with plasma proteins. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.
20:309-323 (2005) Review. Mera K, Anraku M, Kitamura K, Nakajou K, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. The structure and function of oxidized albumin in hemodialysis patients: Its role in elevated oxidative stress via neutrophil burst. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:1322-1328 (2005). Nakajou K, Horiuchi S, Sakai M, Hirata K, Tanaka M, Takeya M, Kai T, Otagiri M. CD36 Is not involved in scavenger receptor-mediated endocytic uptake of glycolaldehyde- and methylglyoxal-modified proteins by liver endothelial cells. J. Biochem. 137:607-616 (2005). Kawasaki CI, Nishi R, Uekihara S, Hayano S, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. How tightly can a drug be bound to a protein and still be removable by charcoal hemoperfusion in overdose cases? Clin Toxicol. 43:95-99 (2005). Nakajou K, Horiuchi S, Sakai M, Haraguchi N, Tanaka M, Takeya M, Otagiri M. Renal clearance of glycolaldehyde- and methylglyoxal-modified proteins in mice is mediated by mesangial cells through a class A scavenger receptor (SR-A). Diabetologia 48:317-327 (2005). Takamura N, Maruyama T, Chosa E, Kawai K, Tsutsumi Y, Uryu Y, Yamasaki K, Deguchi T, Otagiri M. Bucolome, a potent binding inhibitor for furosemide, alters the pharmacokinetics and diuretic effect of furosemide: potential for use of bucolome to restore diuretic response in nephrotic syndrome. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33:596-602 (2005). Kragh-Hansen U, Saito S, Nishi K, Anraku M, Otagiri M. Effect of
genetic variation on the thermal stability of human serum albumin. Fukuzawa K, Saitoh Y, Akai K, Kogure K, Ueno S, Tokumura A, Otagiri M, Shibata A. Antioxidant effect of bovine serum albumin on membrane lipid peroxidation induced by iron chelate and superoxide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1668:145-155 (2005). Komatsu T, Oguro Y, Teramura Y, Takeoka S, Okai J, Anraku M, Otagiri M, Tsuchida E. Physicochemical characterization of cross-linked human serum albumin dimer and its synthetic heme hybrid as an oxygen carrier. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1675:21-31 (2004). Harada D, Anraku M, Fukuda H, Naito S, Harada K, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Kinetic studies of covalent binding between N-acetyl-L-cysteine and human serum albumin through a mixed-disulfide using an N-methylpyridinium polymer-based column. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet.19:297-302 (2004). Yamasaki K, Maruyama T, Takadate A, Suenaga A, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Characterization of site I of human serum albumin using spectroscopic analyses: Locational relations between regions Ib and Ic of site I. J Pharm. Sci. 93:3004-3012 (2004). Anraku M, Tsurusaki Y, Watanabe H, Maruyama T, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Stabilizing mechanisms in commercial albumin preparations: octanoate and N-acetyl-l-tryptophanate protect human serum albumin against heat and oxidative stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1702:9-17 (2004). Matsushita S, Isima Y, Chuang VT, Watanabe H, Tanase S, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Functional analysis of recombinant human serum albumin domains for pharmaceutical applications. Pharm. Res. 21:1926-1934 (2004). Anraku M, Kitamura K, Shinohara A, Adachi M, Suenaga A, Maruyama
T, Miyanaka K, Miyoshi T, Shiraishi N, Nonoguchi H, Otagiri M, and
Tomita K. Intravenous iron administration induces oxidation of serum
albumin in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 66:
841-848 (2004). Anraku M, Maruyama T, and Otagiri M. Structural property of albumin - drug binding sites and dosage plan. J. Med. Tech. 48:521-526 (2004). in Japanese. Sakurai Y, Ma SF, Watanabe H, Yamaotsu N, Hirono S, Kurono Y, Kragh-Hansen
U, Otagiri M. Esterase-like activity of serum albumin: characterization
of its structural chemistry using p-nitrophenyl esters as substrates.
Pharm. Res. 21: 285-292 (2004). Nakajou K, Watanabe H, Kragh-Hansen U, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. The
effect of glycation on the structure, function and biological fate
of human serum albumin as revealed by recombinant mutants. Biochim.
Biophys. Acta 1623: 88-97 (2003). Anraku M, Kragh-Hansen U, Kawai K, Maruyama T, Yamasaki Y, Takakura
Y, Otagiri M. Validation of the chloramine-T induced oxidation of
human serum albumin as a model for oxidative damage in vivo. Pharm.
Res. 20: 684-692 (2003). Harada D, Naito S, Otagiri M. Kinetic analysis of covalent binding
between N-acetyl-L-cysteine and albumin through the formation of
mixed disulfides in human and rat serum in vitro. Pharm. Res.
19:1648-1654 (2002). Chuang VT, Otagiri M. How do fatty acids cause allosteric binding
of drugs to human serum albumin? Pharm. Res. 19:1458-1464
(2002). Kragh-Hansen U, Chuang VT, Otagiri M. Practical aspects of the
ligand-binding and enzymatic properties of human serum albumin.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25: 695-704. Review (2002). Chuang VT, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Pharmaceutical strategies
utilizing recombinant human serum albumin. Pharm. Res. 19:
569-577. Review (2002). Harada D, Naito S, Hiraoka I, Otagiri M. In vivo kinetic analysis of covalent binding between N-acetyl-L-cysteine and plasma protein through the formation of mixed disulfide in rats. Pharm. Res. 19:615-620 (2002). Watanabe H, Yamasaki K, Kragh-Hansen U, Tanase S, Harada K, Suenaga
A, Otagiri M. In vitro and in vivo properties of recombinant human
serum albumin from Pichia pastoris purified by a method of short
processing time. Pharm. Res. 18: 1775-1781 (2002).
Anraku M, Yamasaki K, Maruyama T, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Effect
of oxidative stress on the structure and function of human serum
albumin. Pharm. Res. 18:632-639 (2001). Harada D, Naito S, Kawauchi Y, Ishikawa K, Koshitani O, Hiraoka I, Otagiri M. Determination of reduced, protein-unbound, and total concentrations of N-acetyl-L-cysteine and L-cysteine in rat plasma by postcolumn ligand substitution high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 290:251-259 (2001). Sakai T, Yamasaki K, Sako T, Kragh-Hansen U, Suenaga A, Otagiri
M. Interaction mechanism between indoxyl sulfate, a typical uremic
toxin bound to site II, and ligands bound to site I of human serum
albumin. Pharm. Res. 18: 520-524 (2001). Watanabe H, Kragh-Hansen U, Tanase S, Nakajou K, Mitarai M, Iwao
Y, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Conformational stability and warfarin-binding
properties of human serum albumin studied by recombinant mutants.
Biochem. J. 357: 269-274 (2001). Chuang VT, Otagiri M. Flunitrazepam, a 7-nitro-1,4-benzodiazepine
that is unable to bind to the indole-benzodiazepine site of human
serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1546: 337-345
(2001). Watanabe H, Tanase S, Nakajou K, Maruyama T, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M.Role of arg-410 and tyr-411 in human serum albumin for ligand binding and esterase-like activity. Biochem. J. 349: 813-819 (2001). Watanebe H, Maruyama T, and Otagiri M. A topological analysis of the drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Xenobio. Metabol. and Dispos. 16:264-270 (2001). in Japanese. Maruyama T and Otagiri M. Application of serum albumin to drug delivery system. Artificial Blood 9:88-94 (2001). in Japanese. Yamasaki K, Rahman MH, Tsutsumi Y, Maruyama T, Ahmed S, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Circular dichroism simulation shows a site-II-to-site-I displacement of human serum albumin-bound diclofenac by ibuprofen. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 14: E12 (2000). Kawasaki C, Nishi R, Uekihara S, Hayano S, Otagiri M. Charcoal hemoperfusion in the treatment of phenytoin overdose. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 35:323-326 (2000). Kawasaki C and Otagiri M. Effectiveness and its prediction of charcoal hemoperfusion treatment in drug overdose: A guideline based on the protein binding percentage of the drug. Xenobio. Metabol. and Dispos. 15:275-280 (2000). in Japanese. |
|||