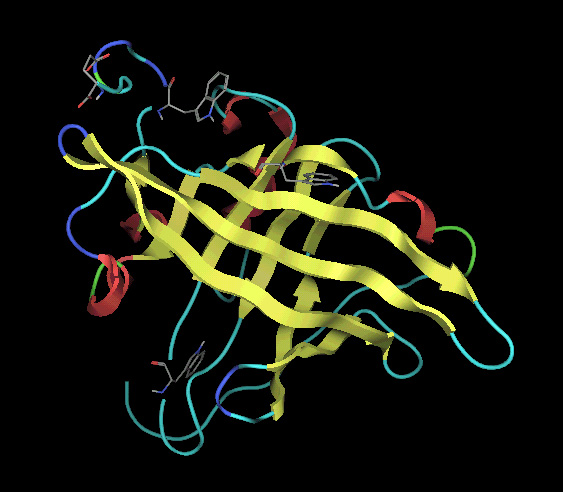
α1-酸性糖蛋白質 (AGP)は、183個のアミノ酸と5本の糖鎖からなる糖蛋白質で、血中では主に塩基性薬物を結合しています。これまでに,我々はAGPが塩基性薬物,酸性薬物及びステロイドホルモンがお互いに重なり合うような幅広い結合領域を保持していることを提唱してきました。このような血清蛋白分子上の薬物結合サイトの同定が,薬物相互作用の予測に役立つことは言うまでもないことです。
その一方で、生体内に存在するAGPが最終的に血液からどの組織に移行し、その一生を終えるのかは全く分かっていません。この問題を解明することは、AGPに結合した薬物の運命、さらには未だに解明されていないAGPの生理機能を知る上でも重要になってきます。
当研究室では以下のテーマについて研究を進めています。
1.光アフィニティラベル法によるAGP分子上の薬物結合部位のマッピング
2.生体膜とAGPの相互作用による構造及び機能変化に関する検討
3.AGPの血中消失に関与する糖鎖及び受容体の解明
4.急性炎症時におけるAGPの生体保護機構の解明
研究業績(2000〜)
Nishi K, Ueno M, Murakami Y, Fukunaga N, Akuta T, Kadowaki D, Watanabe H, Suenaga A, Maruyama T,Otagiri M, A site-directed mutagenesis study of drug-binding selectivity in genetic variants of human alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein. J Pharm Sci, in press (2009).
Matsumoto K, Nishi K, Kikuchi M, Kadowaki D, Tokutomi Y, Tokutomi N, Nishi K, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Alpha1-acid glycoprotein suppresses rat acute inflammatory paw edema through the inhibition of neutrophils activation and prostaglandin E2 generation. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1226-1230 (2007)
Nishi K, Komine Y, Fukunaga N, Maruyama T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Related Articles, Links Involvement of disulfide bonds and histidine 172 in a unique beta-sheet to alpha-helix transition of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein at the biomembrane interface. Proteins. 63:611-620 (2006)
Nishi K, Komine Y, Sakai N, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. Cooperative effect of hydrophobic and electrostatic forces on alcohol-induced alpha-helix formation of alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein. FEBS Lett. 579:3596-3600 (2005).
Katsuki M, Chuang VT, Nishi K, Kawahara K, Nakayama H, Yamaotsu N, Hirono S, Otagiri M. Use of photoaffinity labeling and site directed mutagenesis for identification of key residue responsible for extraordinarily high affinity binding of UCN-01 in human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 280:1384-1391 (2005).
Nishi K, Fukunaga N, Otagiri M. Construction of expression system for human alpha1-acid glycoprotein in Pichia pastoris and evaluationof its drub binding properties. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 32:1069-1074 (2004).
Nishi K, Maruyama T, Halsall HB, Handa T, Otagiri M. Binding of alpha1-acid
glycoprotein to membrane results in a unique structural change and ligand
release. Biochemistry 43:10513-10519 (2004).
Katsuki M, Chuang VTG, Nishi K, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Tryptophan residues play an important role in the extraordinarily high affinity binding interaction of UCN-01 to human alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Pharm Res. 21:1648-1655 (2004).
Tokutomi Y, Okamoto S, Matsumoto K, Otagiri M, Nishi K, Tokutomi N. Effects of alpha1-acid glycoprotein on isometric tension of mouse aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 477:137-141 (2003).
Matsumoto K, Nishi K, Tokutomi Y, Irie T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M. Effects
of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein on erythrocyte deformability and membrane
stabilization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26:123-126 (2003).
Matsumoto K, Sukimoto K, Nishi K, Maruyama T, Suenaga A, Otagiri M.Characterization
of ligand binding sites on the alpha1-acid glycoprotein in humans, bovines
and dogs. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokin. 17:300-306 (2002).
Nishi K, Sakai N, Komine Y, Maruyama T, Halsall HB, Otagiri M. Structural
and drug-binding properties of alpha1-acid glycoprotein in reverse micelles.Biochim
Biophys Acta 1601:185-191 (2002).
Komori T, Kai H, Shimoishi K, Kabu K, Nonaka A, Maruyama T, Tamura K,
Otagiri M. Up-regulation by clarithromycin of alpha1-acid glycoprotein
expression in liver and primary cultured hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol.
62:1391-1397 (2001).
Shimoishi K, Kai H, Kabu K, Komori T, Maruyama T, Otagiri M. FK506 (tacrolimus) increases rat alpha1-acid glycoprotein expression in liver and primary cultured hepatocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 420:91-95 (2001).
日本語総説
松元一明, 岡本茂洋, 徳富芳子, 徳富直史, 西 勝英, 丸山 徹, 末永綾香, 小田切優樹. α1-酸性糖蛋白質の血液循環系に及ぼす作用. 人工血液 11:144-150 (2003).